
Note: This optimised design is quite different to the arm in the photo, and would need to be manufactured differently.

An ideal design will have stresses as unifrom as possible. This diagram shows a computer analysis where colours represent different stresses. The cross-section of the beam is increased where the amount of bending is highest. The upper and lower flanges take most of the load (tension/compression), and the vertical web simply holds the two flanges together (shear).Įxample of a loader arm optimised for bending. However, the upper and lower flanges must be held together to prevent slipping. Most of the area is concentrated as far away as possible away from the centroid (middle of area). So the best way to get a high Second Moment of Area is to get as much area as possible the longest distance from the centre axis (Called the centroidal axis or neutral plane). Second Moment of Area of a cross-section is found by taking each mm 2 and multiplying by the square of the distance from an axis. Where b is breadth (horizontal) and h is height (vertical) if the load is vertical - e.g. Orientation can change the second moment of area (I). The second moment of area is a measure of the 'efficiency' of a cross-sectional shape to resist bending caused by loading.īoth beams have the same area and even the same shape.īeam 1 is stronger than Beam 2 because it has a higher second moment of area (I). The second moment of area is also known as the moment of inertia of a shape.
#Moment of inertia of a circle a rod vs tube plus#
Graphics is a screen share of this web page plus tablet sketching. The Centroid Starting from simple I and finishing at the centroid for a combined element cross-section.
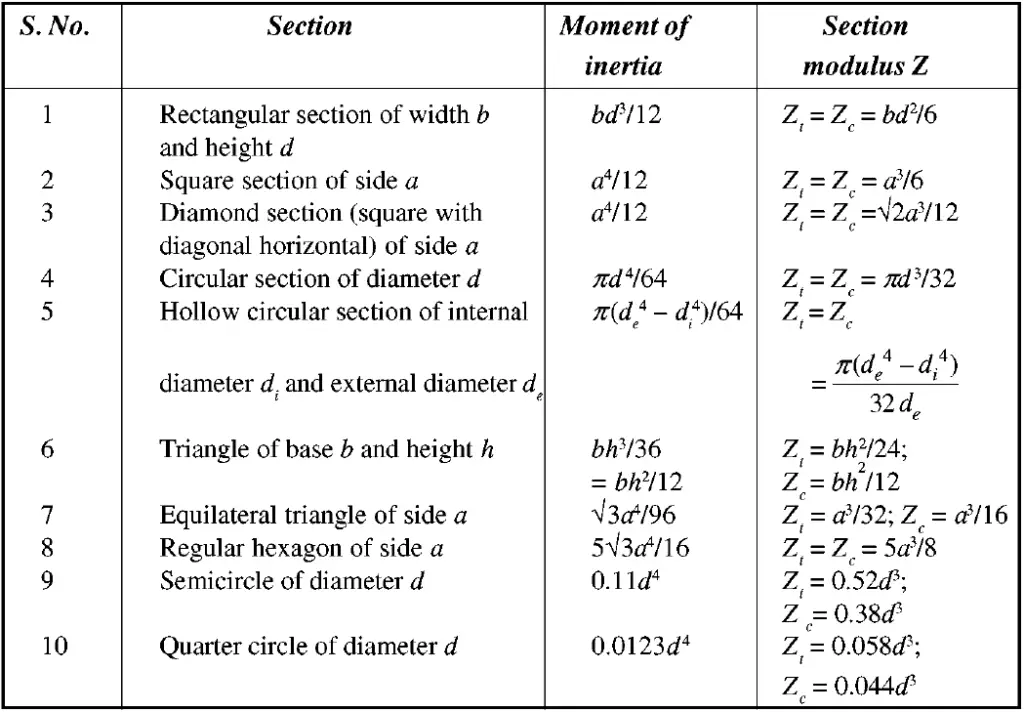
From "Why do we need it?" to calculating I for simple shapes. The Introduction to Second Moment of Area Graphics is a screen share of this web page plus tablet sketching. Calculating I for a complex shapes where the centroids of each element are not at the same height. Formulas for I of simple shapes.Īrea Moments (part 2) Combined shapes. Lecture Notes: Area-Moment.pdf Area-Moment.oneĪrea Moments (part 1) Introducing I (the Second moment of area) and why it is used for bending situations. It is the special "area" used in calculating stress in a beam cross-section during BENDING.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
